Is there a high probability of benign rectal tumors?
In fact, the probability of benign and malignant tumors of the rectum is half of each, almost the same. Distinguish between benign and malignant must be confirmed by pathology.
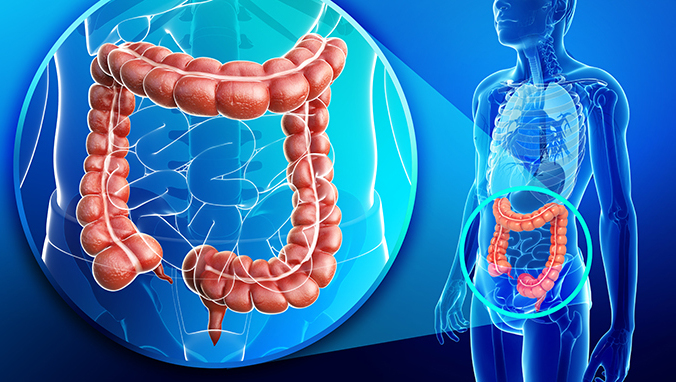
benign and malignant rectal tumors What is the difference?
A benign tumor refers to the abnormal proliferation of cells in certain tissues in the body, showing an expansive growth. It is easy to remove cleanly during the operation, without removal and no recurrence. Malignant tumors are diseases caused by abnormal mechanisms controlling cell growth and proliferation. Cancer cells grow out of control, and can also invade surrounding normal tissues locally or even transfer to other parts of the body through the circulatory system or lymphatic system of the body.
And the benign growth is generally slow, and it grows expansively, clearly demarcating from the surrounding tissues, and the tumor itself has no ulcers or bleeding. Malignant tumors generally grow rapidly and become invasive, with no obvious boundary with the surrounding tissues, and tumors often have bleeding ulcers.
Rectal cancer has an insidious onset. It is often asymptomatic or not obvious at the early stage. It only feels uncomfortable, indigestion, and occult blood in the stool. As the tumor develops, symptoms gradually appear, mainly manifested as changes in stool habits, Abdominal pain, bloody bowel obstruction and other symptoms. And even a benign tumor of the rectum may be transformed into a malignant tumor, so if you have any discomfort or corresponding symptoms, you must go to the hospital for examination early. Rectal cancer is now relatively common. Whether it is a benign tumor or malignant, it must be eliminated if it can be eliminated. Even benign tumors of the rectum may become malignant, and it is not possible to pay attention to diet, daily life, especially Don’t stay up late, eat less barbecue and spicy food, and cut off the tumor from the root cause.
Related Articles

- Early Signs of Bladder Cancer
- What are the early symptoms of bladder cancer?
- 2020-12-17

- How to prevent depression
- How to prevent depression?
- 2020-12-17
- Early symptoms of lung cancer
- 2020-12-17

- Symptoms of depression
- What are the symptoms of depression?
- 2020-12-17

- Drinking water can prevent heat stroke
- Actually, the hot weather is not the direct cause of heat stroke. Heat stroke is mostly caused by sweating caused by heat. Under the high temperature in summer, the body sweats tens of tim
- 2020-08-03

- Office workers should beware of cervical spondylosis
- Cervical spondylopathy is mainly caused by degeneration of cervical intervertebral disc and hyperostosis of cervical spine, with neck and shoulder pain, numbness of upper extremities and d
- 2020-08-03
