What is descending colon adenocarcinoma
Colon adenocarcinoma is a common gastrointestinal malignant tumor derived from colon gland epithelium, which belongs to one of various pathological types of colon cancer. The etiology is not yet clear, but the occurrence of this disease is related to a fat-and-fiber-free diet. Adenomatous polyps, schistosomiasis, nonspecific ulcerative colitis, colonic adenocarcinoma bacterial dysentery, and amoebic bowel disease are also related to this disease. Disease occurrence is closely related. 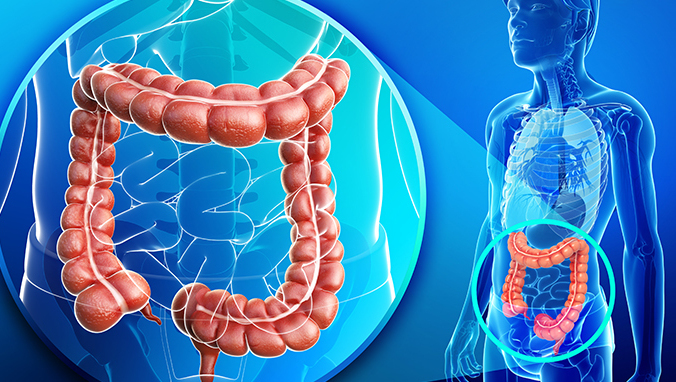
About The colon cancer of 40% is distributed in the rectum and sigmoid flexure of the rectum, and the rest is distributed in the sigmoid colon, cecum, ascending colon, descending colon, transverse colon, liver and splenic flexure. Colon adenocarcinoma is the most common type of colon cancer. The remaining classifications include mucinous adenocarcinoma and undifferentiated carcinoma. The general shape can be polypoid and ulcerative.
The colon cancer is insidious and concealed. In the early stage, only fecal occult blood is positive, and it gradually becomes bloody stools and dysentery-like pus and bloody stools. Alternately, these changes become prominent manifestations of colon cancer. Patients often have varying degrees of abdominal pain, often with erosion, necrosis, and secondary infection. If they occur on the right side, they will produce dull pain in the right abdomen, and sometimes post-meal abdominal pain.
Left colon cancer is often complicated by intestinal obstruction, sometimes with abdominal cramps, accompanied by abdominal distension and hyperactive bowel sounds. Abdominal masses are more common in the right abdomen, which is one of the manifestations of right colon cancer, suggesting that the mid-advanced stage may have a nodular sensation on the surface of the mass, which can generally be propelled, but it is fixed in the late stage of the tumor and may be tender when complicated with infection. Patients with colon cancer may develop progressive anemia, low fever, progressive weight loss, cachexia, hepatomegaly, edema, jaundice and ascites in colon adenocarcinoma, etc.
Chemotherapy of colon adenocarcinoma: Chemotherapy occupies an important position in the treatment of colon adenocarcinoma and can generally be performed after surgery. After surgery, patients can usually use 2 to 3 courses of chemotherapy within one year to one and a half years. The commonly used drugs are mainly 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), and can also be combined with mitomycin and cyclophosphamide. The total amount of 5-FU per course of treatment can be 7 to 10 grams. It can be administered orally or intravenously. It is best to add glucose solution for infusion, 250 mg each time, once a day or every other day.
If adenocarcinoma of the colon has a greater reaction such as nausea, loss of appetite, weakness, decreased white blood cell and platelet counts, etc., the dosage can be reduced or the interval can be increased. When the bone marrow suppression is obvious, the drug can be stopped in time. The gastrointestinal reaction of oral method is greater than that of intravenous administration, but the bone marrow suppression reaction is mild. During medication, care must be taken to support the treatment and to reduce side effects.
Cancer patients who have not been resected with cancer have chemotherapy, which can alleviate the symptoms and control tumor growth, but the effect is poor, and the maintenance time is short. If the patient''s general condition is poor, the side effects are significant, but the condition is worse. , Not suitable for application.
Related Articles
- Early symptoms of lung cancer
- 2020-12-17

- Early Signs of Bladder Cancer
- What are the early symptoms of bladder cancer?
- 2020-12-17
- Is metastatic carcinoma easy to metastasize
- Once the cancer has metastasized, it will be very difficult to cure, because many people have lost their lives because of the emergence of cancer, so most people think that cancer is an un
- 2020-08-02

- What does microinfiltrating adenocarcinoma mean?
- Microinfiltrating adenocarcinoma is a type of lung cancer. The reason why it is called microinfiltration means that there is less infiltration around it, which means that it is in the early
- 2020-08-01
- How long can non-small cell adenocarcinoma live
- Adenocarcinoma is one of the most common malignant tumors in the world. Non-small cell adenocarcinoma accounts for about 80% of all adenocarcinomas. About 75% of patients are in the middle
- 2020-08-01

- Hand cancer
- Finger cancer generally refers to the appearance of skin cancer, which is characterized by local cauliflower-like skin and easy bleeding. Finger skin cancer is mostly a malignant tumor that
- 2020-08-01
