Is adrenal medulla tumor serious?
Is adrenal medulla tumor serious? The adrenal gland is an important endocrine gland in the human body, which plays a very important role in regulation and control, but the more important parts are more susceptible to disease invasion, adrenal medulloma is relatively rare in our daily life It is rarely heard, but its harmfulness should not be underestimated. So, is adrenal medulloma serious?

Adrenal medullary adenoma is a tumor that occurs in the chromaffin tissue of the adrenal medulla, sympathetic ganglia, parasympathetic ganglia, or other parts. This kind of tumor continuously or indirectly releases a large amount of catecholamines, causing endocrine disease with onset hypertension and sympathetic nerve excitation as the main clinical manifestation. Severe attacks can cause cardiovascular and cerebrovascular accidents and endanger the patient''s life.
If diagnosed early, benign adrenal medullary adenoma can be cured by surgery. The disease is a rare secondary hypertension, with a prevalence rate of 0.1%~1%. In recent years, with the development of medicine and the increased vigilance of doctors, the discovery of this disease has gradually increased. The incidence of men and women is similar, and it can occur in all age groups. ~50 years old is the most common, there are many children patients.
Pediatric patients have a male to female ratio of 2:1. The disease may have a family history and is called familial adrenal medullary adenoma. It belongs to type Ⅱ and Ⅲ in multiple endocrine adenoma. 80%~90%, malignant account for 10%~2 0%. The diameter of the tumor is about 12 to 16 cm, the weight ranges from several grams to 3 kg, and the size varies, generally around 100 grams.
Approximately 80% Adrenal medullary adenoma is found in the adrenal medulla, but it can also be found in other tissues from neurospinal cells. The adrenal medullary tumor is equal in both sexes, bilateral 10%(Child 20& #xFF05;), usually benign (95%), extraadrenal tumors are more malignant (30%), although adrenal medullary adenoma can be seen at any age, but the maximum incidence is between 20-50 years.
The clinical manifestations are caused by tumor cells secreting large amounts of catecholamines. Adrenal pheochromocytoma mainly secretes epinephrine. The pheochromocytoma outside the adrenal gland mainly secretes norepinephrine, which is due to the lack of methyl transferase in ectopic tumor tissue. Catecholamines secreted by pheochromocytoma can be intermittent or continuous, resulting in variable clinical symptoms.
Related Articles
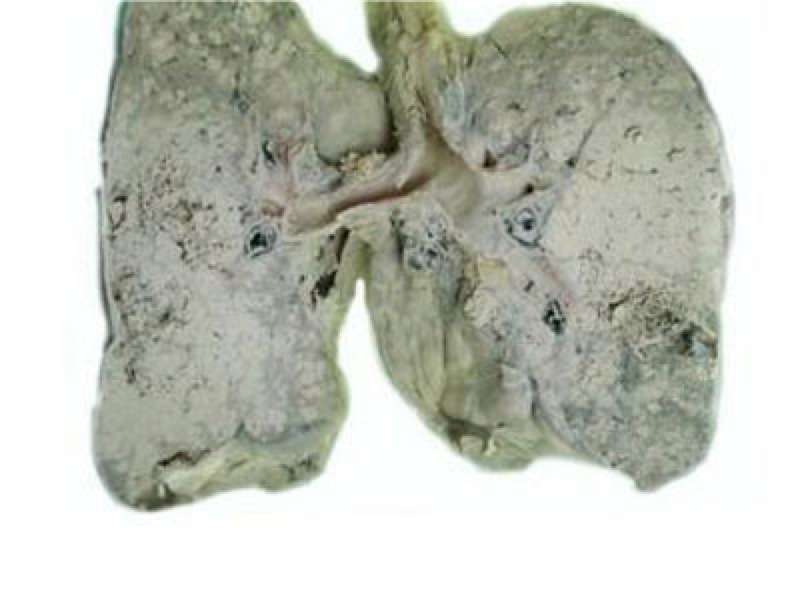
- Early symptoms of lung cancer
- 2020-12-17

- Early Signs of Bladder Cancer
- What are the early symptoms of bladder cancer?
- 2020-12-17
- First-line chemotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma is abbreviated as squamous cell carcinoma, also known as epidermal carcinoma. It is a malignant tumor that occurs in epidermal or accessory organ cells. Cancer cells
- 2020-08-02
- Is the second-grade clear kidney cancer living up to 5 years?
- Nuclear grading is an important prognostic factor for renal clear cell carcinoma and has been included in the WHO classification. Currently, a four-level grading system is generally used. T
- 2020-08-02
- Is metastatic carcinoma easy to metastasize
- Once the cancer has metastasized, it will be very difficult to cure, because many people have lost their lives because of the emergence of cancer, so most people think that cancer is an un
- 2020-08-02

- What does microinfiltrating adenocarcinoma mean?
- Microinfiltrating adenocarcinoma is a type of lung cancer. The reason why it is called microinfiltration means that there is less infiltration around it, which means that it is in the early
- 2020-08-01
